Will taurine supplements make you live longer?
A new study in the journal Science points to taurine deficiency as a driving factor in aging. The study examined taurine levels in mice, monkeys and humans and found that levels declined with age. The researchers then used laboratory mice to determine if supplemental taurine could increase lifespan. The results showed that the median lifespan increased by 10 to 12%.
Important for healthspan:
The study results showed that starting taurine supplementation in midlife “improved functioning of bone, muscle, pancreas, brain, fat, gut, and immune system, indicating an overall increase in health span.”[ref]
Here’s the graphical abstract from the study:
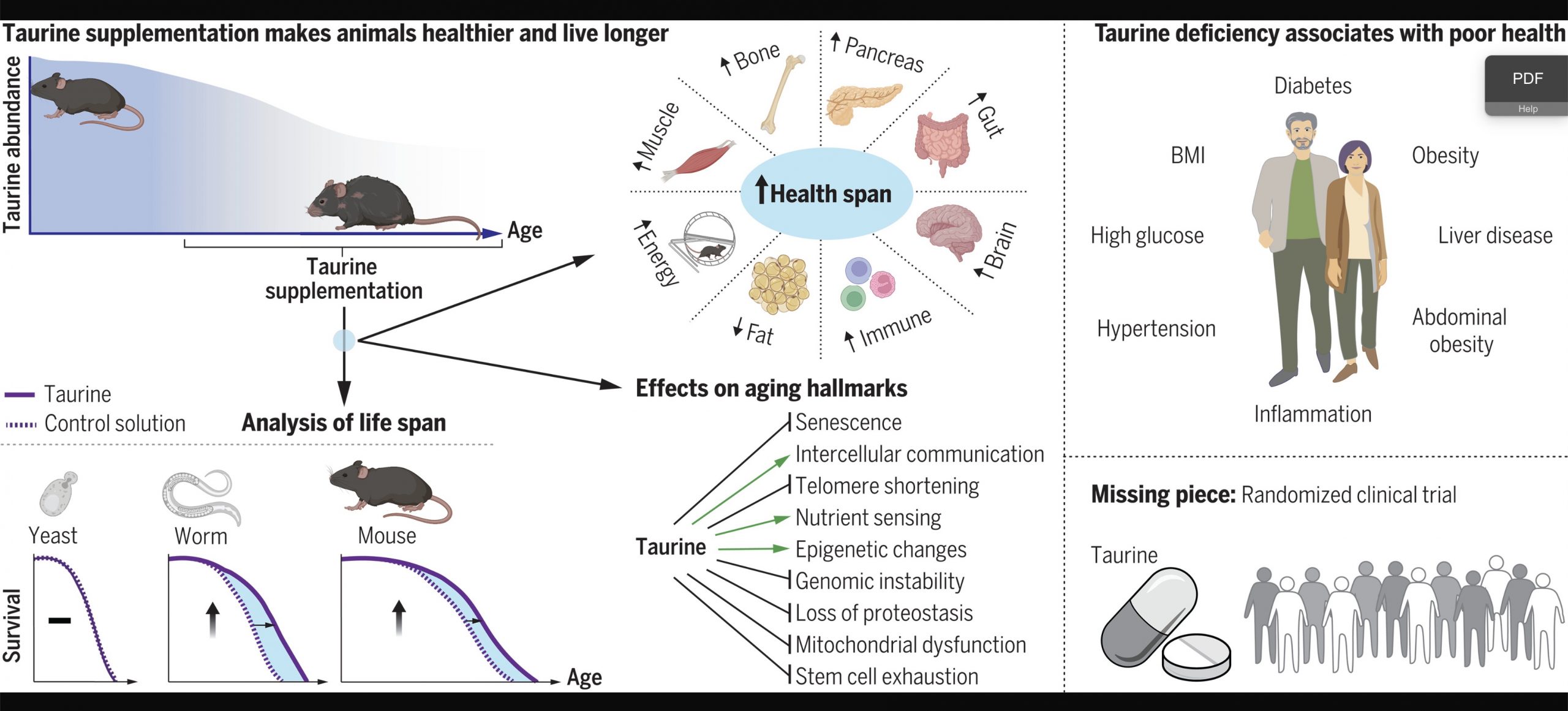
This seems like a no-brainer. Supplemental taurine is readily available as a powder, in capsules, or as part of the TUDCA bile acid conjugate (possibly important in Alzheimer’s).
However, there are no human studies on the longevity effects of taurine. So we don’t really know if it extends lifespan or how much it improves healthspan in humans.
What exactly is taurine?
Taurine is a sulfur-containing amino acid found throughout the body. The liver can make a small amount of taurine by metabolizing cysteine. However, humans get most of their taurine from foods such as beef, shellfish, and the dark meat of chicken. It is also found in energy drinks such as Red Bull and Monster.[ref]
Let’s take a look at what we do know from randomized placebo-controlled clinical trials using taurine:
Clinical Trials with Taurine:
Mitochondrial health:
In patients with MELAS (mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis and stroke-like episodes), taurine reduced the stroke-like episodes by half in over 80% of clinical trial participants.[ref]
Fatty acid oxidation:
Supplemental taurine increased fatty acid oxidation in obese women when combined with exercise.[ref] Similarly, taurine increased lipid metabolism in young, healthy men doing moderate-intensity exercise.[ref]
Reduces blood pressure:
In people with prehypertension, taurine supplementation reduced blood pressure in a placebo-controlled clinical trial. The trial used 1.6 g per day (or a placebo) for 12 weeks. Taurine supplementation significantly decreased systolic blood pressure on average by 7.2 mm Hg and diastolic BP by 4.7 mm Hg. [ref]
Anti-inflammatory and anti-atherogenic:
In patients with heart failure, taurine supplementation (1500mg/day for two weeks) reduced CRP levels and showed beneficial effects on atherogenic indices.[ref]
Heart function capacity:
In heart failure patients, taurine supplementation “enhanced the physical function and significantly reduced the cardiovascular function parameters following exercise. Our results also suggest that the short-term taurine supplementation is an effective strategy for improving some selected hemodynamic parameters in heart failure patients.”[ref]
Heat endurance in athletes:
Taurine supplementation (50mg/kg) increased cycling time duration for athletes exercising in the heat. It also decreased core temperature and lactic acid production.[ref]
Advanced glycation end products:
Taurine supplementation (3,000 mg/day) reduces advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and improves glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes.[ref]
Supplementing with taurine:
The above clinical trials used 1,500 – 3,000 mg/day, usually divided into two or three doses.
For higher doses, you’ll end up taking a lot of capsules, if you go that route. Personally, I tend to go with the pure powdered supplement for something that doesn’t taste bad and is used in gram doses.
Taurine in powder form is easy to mix into a drink or smoothie. Here’s one option for powdered taurine.
If you don’t like the hassle of measuring out powdered taurine, there are many options for getting it in capsules, such as from Thorne or Pure Encapsulation. Read the reviews and choose a brand you trust.
Taurine can also be found in bile acid supplements, so check to see how much you are getting if you are also taking TUDCA or another bile acid.
Cordyceps mushrooms contain up to 1mg of taurine per gram.[ref]
Food sources of taurine:
Adapted from Table 2 in PMC2813349
| Food | Method of Preparation | Mean Taurine Content mg/100g |
|---|---|---|
| Beef | Raw | 43.1 mg/100 g |
| Broiled | 38.4 | |
| Chicken dark meat | Raw | 82.6 – 169.6 |
| Broiled | 199.1 | |
| Chicken light meat | Raw | 17.5 |
| Broiled | 14.5 | |
| Turkey dark meat | Raw | 306 |
| Roasted | 299.6 | |
| Turkey light meat | Raw | 29.5 |
| Roasted | 11.1 | |
| Veal | Raw | 39.8 |
| Broiled | 46.7 | |
| Pork, loin | Raw | 50.1 -61.2 |
| Roasted | 56.8 | |
| Lamb dark meat | Raw | 43.8 -47 |
| Ham, picnic | Baked | 49.8 |
| Salami, cotto beef | Cured | 59.2 |
| Bologna, pork/beef | Cured | 31.4 |
| Bologna, turkey | Cured | 122.7 |
| Tuna, albacore | Canned | 41.5 |
| Tuna, chunk light | 39 | |
| White fish | Raw | 113.9 -151.2 |
| Cooked | 172.1 | |
| Shrimp, small | Cooked | 10.5 |
| Shrimp, medium | Raw | 39.4 |
| Mussels | Raw | 655.4 |
| Oysters | Fresh | 70 –396.7 |
| Cod | Frozen | 31 |
| Clams | Raw | 240 – 520.7 |
| Canned | 152 | |
| Octopus | Raw | 388 |
| Scallop | Raw | 827.7 |
| Squid | Raw | 356.7 |
| Cow’s milk | Unprocessed | <0.5 |
| Pasteurized milk | 6 |
Conclusion and Safety:
Even without clinical trials in humans for longevity, there are multiple clinical trials in older adults showing positive results that are related to healthspan (e.g. heart function, blood pressure reduction, AGEs, mitochondrial function). What we don’t know is the optimal dose and timing…
Safety studies and clinical trials showed no significant adverse effects at intakes of 3g/day. One study did use up to 10 grams per day for six months. [ref]
Talk with your doctor, of course, if you have any questions on taurine – especially if you are on prescription medications.
